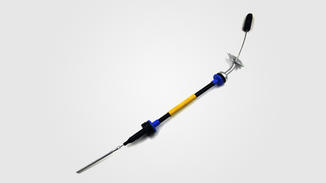
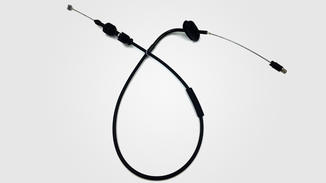
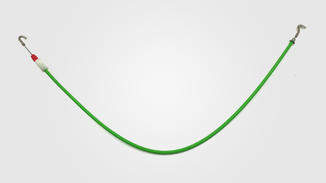
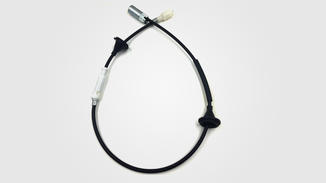
Automotive control cables do indeed require the use of corrosion inhibitors in specific situations, which mainly depend on the operating environment, material characteristics, and potential corrosion risks that the cable may face.
Firstly, automotive control cables are typically exposed to complex and variable environments such as high temperatures, humidity, salt spray, oil stains, etc., all of which can accelerate the corrosion process of the cables. Especially in coastal areas or harsh weather conditions, cables are more susceptible to salt spray and moisture erosion, cause to problems such as metal oxidation and insulation layer aging.
Secondly, metal parts in automotive control cables, such as copper or aluminum wires, may cause electrochemical corrosion due to potential differences with other metals or materials. Especially at connection points such as cable joints and terminals, due to poor contact or the presence of electrolytes caused by environmental factors, electrochemical corrosion is more likely to occur, which in turn affects the conductivity and overall lifespan of the cable.
To effectively prevent or mitigate the corrosion problem of automotive control cables, using corrosion inhibitors is a feasible solution. Corrosion inhibitors can form a protective film on the surface of cables, isolating external environmental erosion and reducing the dissolution rate of metal parts in electrolytes, thereby extending the service life of cables.
It should be noted that the selection of appropriate corrosion inhibitors should be comprehensively considered based on factors such as the specific material of the cable, operating environment, and expected service life. In addition, when using corrosion inhibitors, relevant operating procedures and safety requirements should be followed to ensure the safety and reliability of the cables.

 简体中文
简体中文